Antwort How many steps does PCR take? Weitere Antworten – What are the steps of the PCR

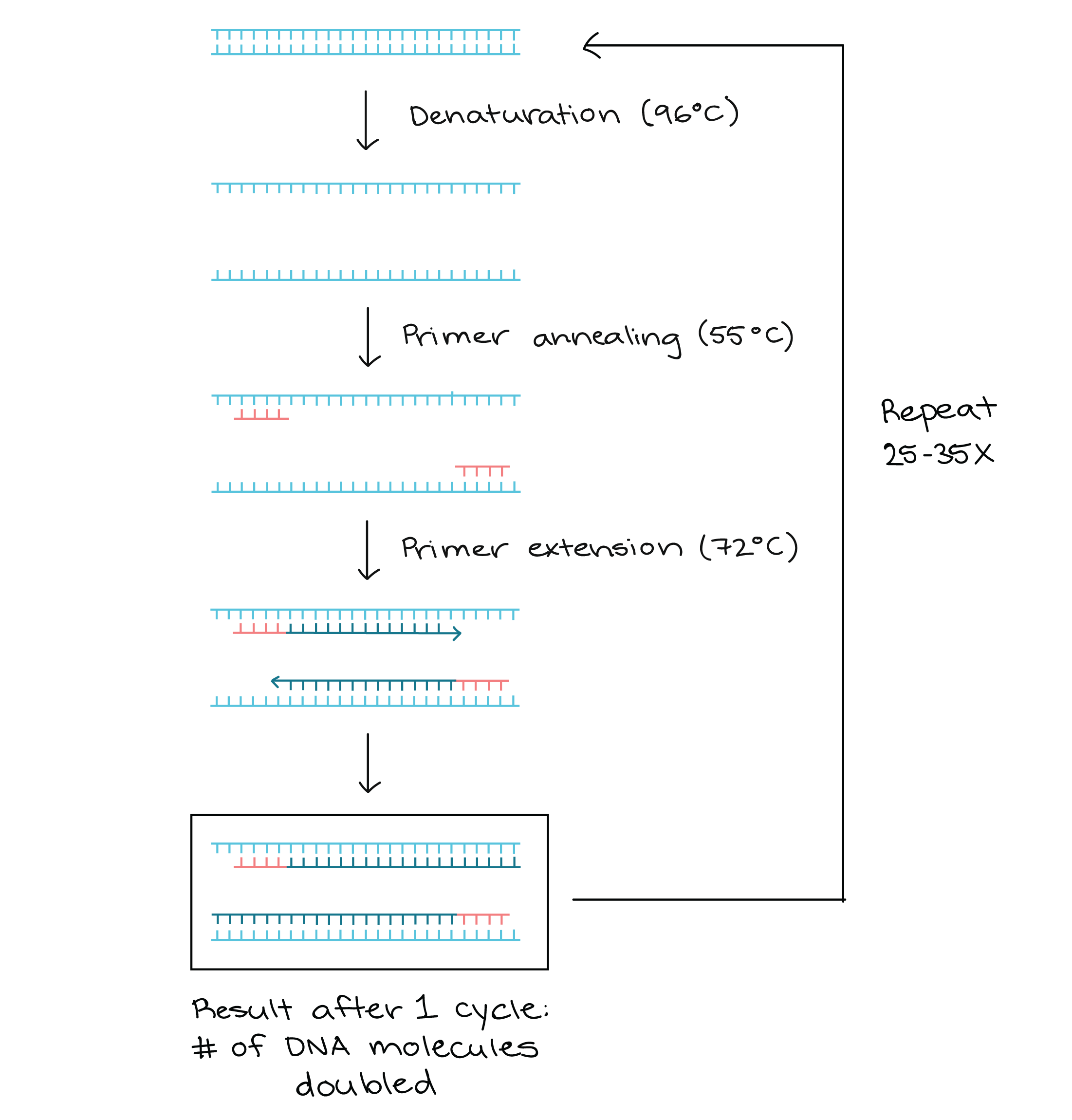
The tube is placed into the PCR machine or thermal cycler. The thermal cycler takes the solution through a 3-step process: denaturation, annealing, and extension.The entire cycling process of PCR is automated and can be completed in just a few hours. It is directed by a machine called a thermocycler, which is programmed to alter the temperature of the reaction every few minutes to allow DNA denaturing and synthesis.PCR cycling | PCR cycle number determination
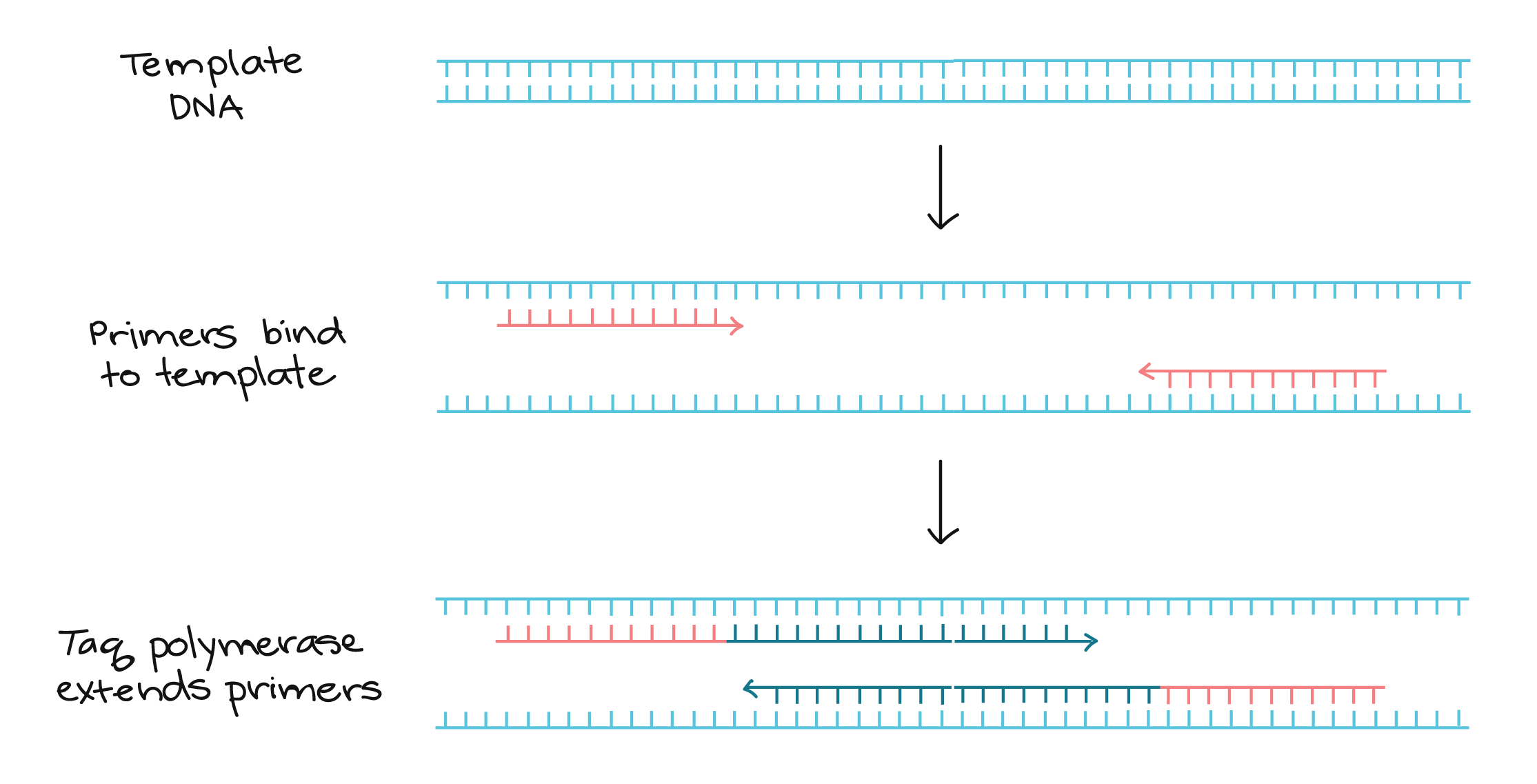
In theory, each PCR cycle doubles the amount of amplicon in the reaction. Therefore, 10 cycles multiply the amplicon by a factor of ~1000 and so on. Each PCR cycle consists of template denaturation, primer annealing and primer extension.
How long for extension PCR : 20 sec to 1 min
The final stage is the extension step (20 sec to 1 min at 72 °C), which is performed so that the DNA polymerase extends the primer sequences from the 3' of each primer to the end of the amplicon. A 1 min extension is typically sufficient to synthesize PCR fragments up to 2 kilobases (kb).
How many copies of DNA after 10 cycles of PCR
1024 copies
The number of double stranded DNA pieces is doubled in each cycle, so that after n cycles you have 2^n (2 to the n:th power) copies of DNA. For example, after 10 cycles you have 1024 copies, after 20 cycles you have about one million copies, etc.
What is two step PCR : Two-step RT-PCR entails two separate reactions, beginning with first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT), followed by amplification of a portion of the resulting cDNA by PCR in a separate tube. Therefore, two-step RT-PCR is useful for detecting multiple genes in a single RNA sample.
By providing a sufficient amount for analysis or subsequent experimentation, denaturation, annealing, and extension steps exponentially amplify the target DNA during each cycle. For accurate and reliable results, the repetition of cycles ensures that enough DNA is produced.
This is becuase; 1. DNA polymerase after 30-35 cycles is usually denatured, becuse each denaturation temp (95-94) for 30 sec to 1 min effects the protein function and it is not tolerable after 35 cycles usually.
How long is a PCR cycle
Most users of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) would describe it as a fairly fast technique, taking about 45 min to an hour to complete 40 cycles, depending on the particular protocol and instrument used.Most users of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) would describe it as a fairly fast technique, taking about 45 min to an hour to complete 40 cycles, depending on the particular protocol and instrument used.Two-step RT-PCR entails two separate reactions, beginning with first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT), followed by amplification of a portion of the resulting cDNA by PCR in a separate tube. Therefore, two-step RT-PCR is useful for detecting multiple genes in a single RNA sample.
one million copies
The number of double stranded DNA pieces is doubled in each cycle, so that after n cycles you have 2^n (2 to the n:th power) copies of DNA. For example, after 10 cycles you have 1024 copies, after 20 cycles you have about one million copies, etc.
How much DNA after 30 cycles of PCR : After 30 cycles, as many as a billion copies of the target sequence are produced from a single starting molecule.
Does PCR consist of 3 steps : PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
What is one-step vs 2 step PCR
Compared to one-step RT-PCR, the disadvantages of two-step RT-PCR include multiple steps for an extended workflow, additional sample handling and processing, and may increase the chance of contamination and variation in results.
More than 45 cycles is not recommended as nonspecific bands start to appear with higher numbers of cycles. Also, accumulation of by-products and depletion of reaction components drastically lower PCR efficiency, resulting in a characteristic plateau phase for a PCR amplification curve (Figure 7).The three steps are repeated for multiple cycles, with each cycle doubling the amount of DNA in the sample. The number of cycles is determined by the amount of target DNA in the initial sample and the sensitivity required for the experiment.
Is 25 cycles enough for PCR : Generally, 25–35 cycles yields sufficient product. For genomic amplicons, 30–35 cycles are recommended. 2-step PCR: When primers with annealing temperatures ≥ 72°C are used, a 2-step thermocycling protocol (combining annealing and extension into one step) is possible.